
Table of Contents
Introduction: Understanding the E-Waste Crisis
Electronic waste, commonly referred to as “e-waste”, is one of the world’s fastest-growing waste problems, with millions of electronic gadgets becoming obsolete each year due to technology’s advancement and our increasing dependence on it. From laptops and smartphones to IT equipment weighing tons in weight – including laptops containing hazardous substances that could enter our environment, causing considerable harm and worsening health impacts – being dumped unknowingly poses serious environmental hazards that must be managed responsibly to create long-term sustainable solutions. Understanding its scale is the first step toward developing sustainable, responsible solutions.
What is included in E-Waste?
E-waste refers to discarded electrical or electronic devices that are no longer functional or have been replaced by newer models. These include:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktops, televisions, and gaming consoles.
- Household Appliances: Refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, and air conditioners.
- Office and IT Equipment: Servers, networking devices, printers, and data storage systems.
- Industrial and Medical Electronics: Diagnostic machines, monitoring systems, and control equipment.
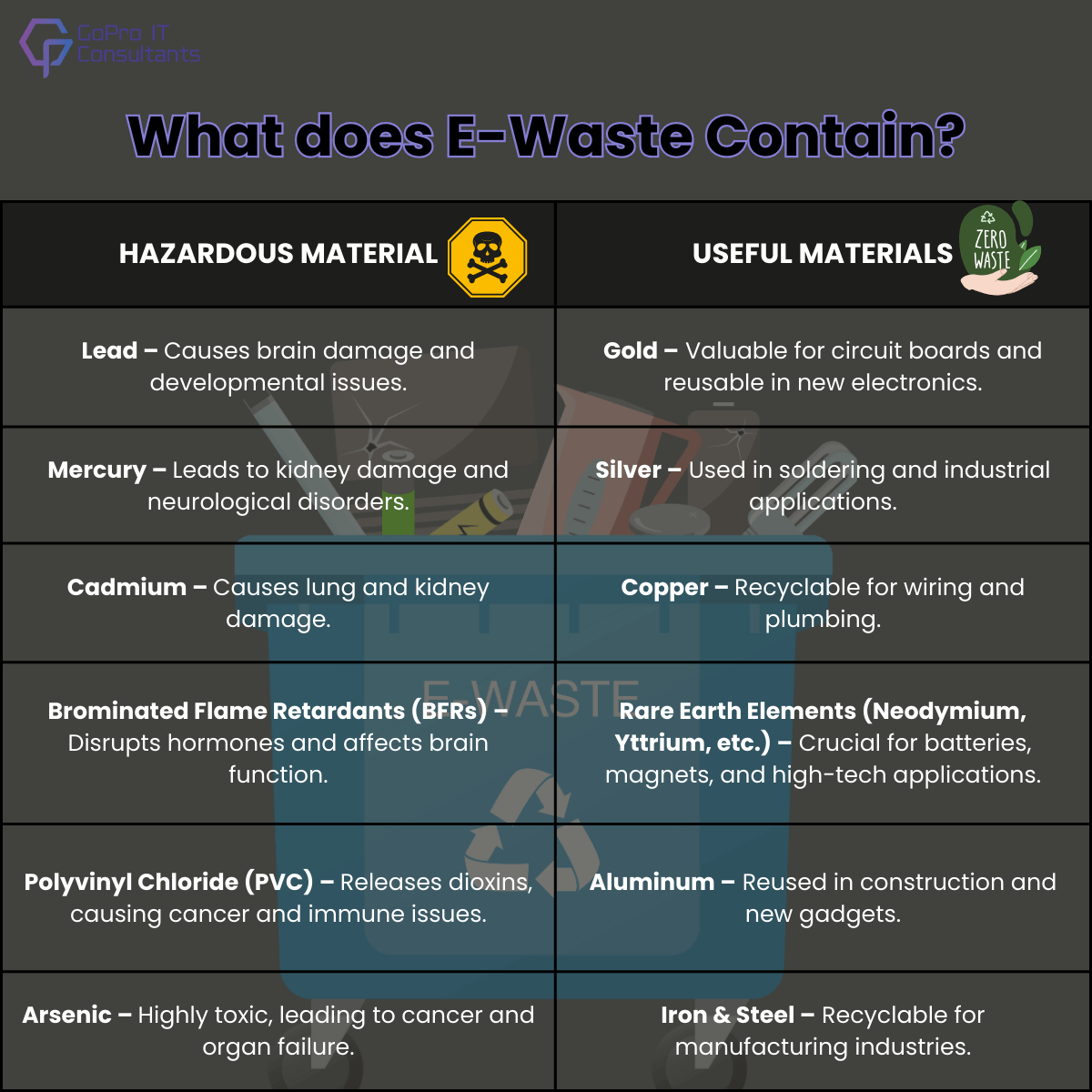
What does E-Waste Contain?
E-waste contains both hazardous and valuable substances. Hazardous substances need to be discarded as they contain harmful substances for the environment. Valuable substances can be recycled and reused for important purposes.
Global E-Waste Trends and Alarming Statistics
Did you know? Every year, we produce more than 50 million tonnes of electronic waste, which is more than 500 Eiffel Towers! Yet only 20 percent of it is recycled. The rest is thrown into landfills, causing harm to humans and the environment. What’s worse? The world is dumping away the equivalent of $57 billion in precious substances such as silver, gold and copper.
If you are thinking of throwing away that old laptop or phone, take a second look! The numbers below may shock you.

These figures highlight the need to adopt environmentally sustainable methods for managing e-waste. Government, businesses and consumers all have a responsibility in reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste by using proper disposal methods and taking the help of IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) service providers and circular economic strategies.
If we examine the causes, problems and possible solutions, it’s clear that solving the issue of e-waste requires an organized effort. Understanding the problem is just an initial step. It is the action that can lead to actual transformation.
Key Drivers Behind the E-Waste Surge
The rapid increase in electronic waste isn’t accidental, it is due to a myriad of interconnected factors that force business and consumers to throw away electronic devices at a faster rate than they have ever. From technological advances that surpass accessibility to a variety of hidden strategies that promote frequent updates, the modern technology environment is causing an electronic waste explosion. Understanding the key drivers is crucial to tackle the problem efficiently.
1. Rapid Technological Advancements and Product Lifecycle Reduction
The rapid pace at which technology advances is awe-inspiring. Each year, we witness speedier processors, sleeker designs, upgraded features, and enhanced functions on our laptops, smartphones, and various electronic devices. Although it is exciting to see innovation, this also implies that the devices are becoming obsolete quickly, reducing their average life span and causing a culture of perpetual replacement.
- A phone that was revolutionary three years ago might be in trouble with software updates.
- A company that invests in the most modern IT infrastructure may be obsolete in five years.
- Modern models usually offer more battery life, more powerful cameras, and better connectivity and make older devices appear less desirable, even though they’re still functioning.
In the end, millions of usable devices are destroyed because they aren’t able to keep up with changing technology or the demands of consumers. The continuous cycle of updates creates e-waste at a rapid rate.
2. Planned Obsolescence: A Hidden Industry Strategy
Not all e-waste is the result of the natural progress in technology. Planned Obsolescence- a deliberate plan used by manufacturers to reduce product life-spans plays an important part in the escalating pollution from e-waste.
What is the process behind this? The design of products by companies is in a manner that restricts their durability, repairability and performance as they age, which forces customers to replace them more often. A few common strategies include:
- Software updates cause slowdowns on older hardware or render them unusable with the latest applications.
- Batteries that are not re-usable and degrade after some years, making repairs difficult.
- Limitations of hardware are a reason why crucial components (like storage or memory) are not upgradeable.
An example that stands out is the mobile industry, which sees manufacturers launch new models that are flagship each calendar year with minor updates that make consumers feel pressured to upgrade to the most recent version. Similar to IT hardware, manufacturers remove the support for older models, which makes them more vulnerable to security risks and compels enterprises to upgrade.
Although planned obsolescence is a major driver of sales, it also increases how quickly electronic devices are destroyed and exacerbates the e-waste problem.
3. Consumer Demand and the Disposable Tech Culture
In the fast-paced world of today, newer is always more efficient– or so we’re led to believe. The emergence of consumerism has created the development of a technology culture that is disposable in which devices are not designed to last but are replaced.
- A lot of people change to the most recent smartphone every two years even if their current phone still functions.
- Businesses regularly replace IT equipment to keep up with the competition.
- Gaming consoles, along with wearables, are continuously updated and make older models look old-fashioned.
Furthermore, affordable electronics and aggressive marketing strategies allow individuals to purchase new devices rather than fix older ones. Why repair a broken laptop instead of buying an entirely new model for an extra few dollars? Why should you change the battery when a new one is through the installment plans?
This mentality has resulted in the throw-away culture in which electronics are considered disposable instead of long-term investments. In the end, the landfills are still stuffed with devices that are discarded, a lot of which are filled with valuable materials that could have been reused by recycling.
Breaking the Cycle: Moving Toward Sustainable Tech Practices
The issue of e-waste won’t be solved until we change these industry practices and change the mindset of consumers. Companies should focus on environmentally sustainable design, long-lasting products, durable devices, or repair models that are more eco-friendly, and consumers should adopt mindful purchasing practices and responsible disposal methods and IT asset Disposition (ITAD) Services to extend the lifespan of their products.
If you are thinking about upgrading your gadget, think about this: Do I require a new device, or am I stuck in the loop? Making informed choices can reduce the amount of e-waste you generate and lead to a more sustainable future.
Environmental and Health Impacts of E-Waste Mismanagement
Inadvertently recycling electronic waste isn’t just an increasing quantity of abandoned gadgets. This is a serious health risk and ecological alarm. Every year, millions of tonnes of electronic waste are dumped in landfills or aren’t properly handled and release poisonous chemicals that harm living organisms and even threaten the lives of humans. The consequences of poor management of electronic waste are immense and affect soils and the water, air, and health of the people managing it in hazardous situations.
We need to discuss the risks that e-waste poses when it is discarded in the absence of adequate control. We will also discuss why we must take urgent action.
1. Hazardous Materials in Electronic Waste
E-waste isn’t your typical trash. It contains a range of dangerous substances that cause serious harm if it is not handled properly. The most hazardous chemicals are:
- Lead: Lead is an element of the circuit board as well as in Cathode Ray Tubes (CRTs) and could cause neurodegeneration, particularly in children.
- Mercury: present in LCD screens and batteries and causes brain and kidney damage.
- Cadmium is used in rechargeable batteries and semiconductors as well as in kidney and lung disease.
- Brominated Fire Retardants (BFRs) – found within plastic casings disrupt the endocrine systems and can cause developmental issues.
If the waste isn’t properly handled, it will leach into the environment, which can pollute the natural resources and expose human beings to health hazards for the long term.
2. Contamination of Soil, Water, and Air
The harmful elements found in e-waste do not stand around in a vacuum; they actively inflict harm on the environment and cause irreparable damage.
- Soil contamination If e-waste gets stored in landfills and disposed of, harmful substances are absorbed into soils, which reduce fertility and damage crops. With time, these chemicals are introduced to the food chain and affect the health of humans and agriculture production.
- Water pollution Heavy Metals, such as mercury and lead, dissolve easily in groundwater and may affect the intake of water for drinking. This could lead to severe health issues, including developmental defects as well as damage to the bodies of children.
- Environmental Pollution Recycling in informal fashion often includes the combustion of electronics to extract precious metals, such as copper and gold. The process releases toxic fumes and dioxins in the air and can trigger respiratory illness and cause global warming.
The longer that e-waste remains in a state of non-treatment, the more environmental damage it will cause, which makes the proper recycling and IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) services essential to the sustainable management of waste.
3. Health Risks for Workers in the Informal Recycling Sector
One of the darkest aspects of the issue of e-waste is the negative impact it can have on recyclers, particularly in the developing world. Because of the lack of protective equipment and safety rules, the majority of recyclers, including women, are exposed to dangerous chemicals every day.
- Direct exposure to hazardous Substances: People handle the e-waste by hand and breathe in toxic gas from the burning of metals and plastics. The result is skin disease and neurologic injuries as time passes.
- Reproductive and developmental issues: The research has proven that exposure to elements such as mercury, lead and cadmium may cause issues with birth as well as miscarriages, cognitive impairments and miscarriages in babies born to parents who were exposed.
- Greater Risk of Cancer: A lot of chemicals found in e-waste, including PCBs, also known as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which are known carcinogens, can increase the chance of lung, liver, and kidney cancers when employed in hazardous recycling settings.
Despite the dangers, the informal processing of e-waste remains commonplace because of the economic imperative and a lack of regulatory oversight. If nothing is done, millions of workers will continue to suffer from the fatal consequences of the unsafe handling of e-waste.
E-Waste Management: Challenges and Current Practices
Controlling the rapid increase in e-waste is an extremely difficult task for anyone around the world. Recycling or responsible disposal are vital solutions, inefficiencies, a lack of regulations, as well as illegal disposal have always impeded progress. To tackle these issues, the best solution is to combine the enforcement of regulations as well as corporate responsibility and an increased awareness of the consumers. The next section will examine the main issues and solutions to the managing of e-waste.
1. The Role of IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) in Responsible E-Waste Recycling
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) provides a method to manage the end-of-life of IT technology in a manner that is safe, eco-friendly, sustainable, and cost-effective. ITAD services can help companies to recover value from old assets, guarantee data security and encourage sustainable recycling methods.
How ITAD Supports Responsible E-Waste Recycling
- Data Security & Compliance: ITAD services ensure that sensitive personal and business data is securely erased or destroyed before recycling devices or sold, assisting organizations in adhering to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
- Refurbishment and resale: Many IT assets remain valuable. ITAD companies evaluate, refurbish and resell functional equipment to extend their lives and decrease the need for new electronic devices.
- Certified Recycling If devices aren’t re-usable, ITAD ensures they are treated through accredited recyclers who adhere to environmentally sustainable recycling methods for electronic waste, which prevents harmful materials from entering landfills.
- Impact on the Circular Economy Repurposing and properly recycling electronic equipment, ITAD plays a vital part in promoting the development of a sustainable and circular economy and reducing the environmental footprint.
Individuals and businesses must prioritize certified ITAD service providers to make sure that outdated devices don’t contribute to the e-waste problem.
2. Legal Frameworks and Global E-Waste Regulations
To tackle the growing issue of e-waste, governments and international organizations have developed regulations that define the proper disposal of e-waste. Yet, enforcement and effectiveness differ across different regions, which creates spaces that allow for improper disposal as well as illegal exports.
Key E-Waste Regulations Around the World
- Basel Convention (Global): A treaty restricting the movement of hazardous waste. It also prohibits advanced nations from dumping e-waste in developing nations.
- WEEE Directive (Europe): Requires manufacturers to be accountable for the collection, treatment and disposal of e-waste and reuse (Extended Producer Responsibility EPR).
- R2 and eStewards Certification (USA and Global): Industry standards for responsible electronics recycling, providing the safety of disposal and data security.
- The Chinese Circular Economy Promotion Law focuses on recycling e-waste and green manufacturing methods.
- The Indian E-Waste Management Regulations: The rules require companies to recycle and collect E-waste using authorized channels.
Challenges in E-Waste Regulation Enforcement
- Uncertainty: While some countries have strict regulations, many do not have formal laws on e-waste that can result in different management procedures.
- Illegal exports: Despite international bans, millions of tons of electronic waste are illegally transported to developing nations, where it is not properly removed, exposing workers as well as the surrounding environment to harmful substances.
- Low Awareness of Consumers: Many consumers and companies are not aware of the proper disposal practices, which leads to the e-waste being disposed of in garbage bins or other recycling areas.
More rigorous enforcement, manufacturer accountability, and global collaboration are required to bridge the gaps and ensure efficient waste management through e-waste.
3. The Dark Side: Illegal E-Waste Dumping and Its Consequences
Despite laws, illegal e-waste dumping is a major global problem. Many countries are not recycling electronic devices properly, sending their electronic waste to nations located in Africa, South Asia, and Latin America, where it is disposed of in unsafe conditions.
Why Does Illegal E-Waste Dumping Happen?
- High Costs for Recycling: Recycling properly requires costly equipment and labour. Some companies cut out the costs of recycling by exporting e-waste illegally to countries that have poor environmental laws.
- Insufficient Implementation: Even with strict laws, such as that of the Basel Convention, loopholes and inadequate enforcement permit illegal shipping in the future.
- Informal recycling economy: For countries including Ghana, Nigeria, and India, unregulated e-waste scrapyards employ employees–including children– who extract metals from electronic components with no safety precautions.
Consequences of Illegal E-Waste Dumping
- Environmental Damage: Toxic Chemicals, such as mercury, lead, and arsenic, are leaking into the water and soil, which contaminate ecosystems.
- Health Risks: Workers exposed to electronic waste suffer from respiratory ailments as well as neurological disorders. They also face elevated cancer risks from long-term exposure to toxic substances.
- lost economic value: instead of saving valuable material by recycling them properly, illegal dumping wastes millions of dollars worth of recyclable resources.
To prevent illegal e-waste disposal, businesses should adopt responsible IT disposal practices, which include cooperating with trustworthy ITAD service providers which assure compliance with global regulations. Connecting with ITAD Service providers like GoProIT Consultants, who have partners from EMEA, APAC, and LATAM– including regions that are prone to the risk of high e-waste- can provide affordable, secure and long-lasting solutions designed to meet the specific needs of businesses.
If they select an accredited ITAD partner, businesses can reduce their environmental footprint as well as protect employees, recycle valuable material and remain fully in line with international e-waste disposal standards.
Sustainable Strategies for E-Waste Reduction
As the issue of electronic waste is growing, businesses, consumers, and even manufacturers should adopt sustainable strategies to reduce electronic waste and minimize the environmental impact. By making conscious decisions, we can prolong the lifespan of electronic devices, minimize unnecessary waste, and support sustainable recycling practices.
1: How Businesses and Consumers Can Minimize E-Waste Generation
For Businesses:
- Install IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) Solutions: Securely refurbish, sell, or recycle old IT equipment.
- Adopt circular Economy Principles: Extend product life by leasing, buy-back programs and repair programs.
- Enhance Awareness for Employees: Educate staff on the proper use of devices, maintenance and appropriate disposal.
For Consumers:
- Extends the life of your device: Regular maintenance, updates to software and repairs may delay the necessity to replace devices.
- Pick Certified recycling programs: Ensure old electronics are removed through trusted recyclers of electronic waste.
- Buy Sustainable Technology: Opt for durable and repairable products from companies that have strong sustainable policies.
2: The Role of Manufacturers in Promoting Sustainability
Manufacturers play an important role in reducing e-waste by developing durable, repairable, and sustainable products. The sustainable initiatives are:
- Eco-Design and Modular Product: Creating devices with modular components that can be replaced to improve usability.
- Recycling & Take-Back Programs: Encourage customers to take back their old devices to ensure responsible recycling.
- Utilization of recycled materials: Reducing raw material consumption by recycling plastics and metals.
Companies that focus on sustainable design in their products and management of lifecycles can help to reduce the burden of e-waste on the planet.
3: Advancements in E-Waste Recycling Technologies
The latest innovations in recycling e-waste improve efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of recycling, for example:
- AI-powered Sorting Systems: Enhancing material recovery rates through the identification and separation of important components.
- Bioleaching and Eco-friendly Extract: Using microbes to remove elements from electronic circuits with no harmful chemicals.
- Closed-loop recycler: Recycling recycled materials into new electronic devices and reducing the need for the use of virgin resources.
In embracing these innovations and these advances, we can develop a more environmentally sustainable and circular method to the management of electronic waste and ensure that fewer devices end up in the garbage.
Future Outlook: The Path to a Sustainable E-Waste Solution
The worldwide issue of electronic waste calls for innovative solutions. more strict rules, and a concerted effort by businesses, governments and consumers. As technology develops, new opportunities emerge, and opportunities are created, so do the possibilities of developing an eco-friendly method of control of electronic waste.
Emerging Technologies in E-Waste Management
The latest technologies are changing the way that E-waste is used to recycle and is treated. The most significant developments are:
- AI & Robotics in E-Waste Sorting: Enhancing efficiency by precise identification and separation of important materials.
- Eco-Friendly Metal Extraction: using methods that use bioleaching as well as chemical-free ones to recover precious metals.
- A closed-loop recycling system: making sure that older electronic devices are utilized for the creation of new products.
With the aid of these technologies, recycling e-waste is expected to be more efficient, economical and environmentally friendly.
The Importance of Circular Economy and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
A circular economy means reducing consumption by making sure that materials and products are used for a longer period. Extended Producer Resilience (EPR) policies hold producers accountable for the full period of their products and encourage:
- Eco-design involves developing devices that are easier to maintain, repair, reuse and recycle.
- Take-Back Programs: These programs offer incentives to consumers to take back their old electronics for proper disposal.
- Sustainable material use: It reduces the use of natural resources through the use of recycled components.
When EPR is implemented, firms are urged to develop environmentally sustainable products instead of disposable ones.
Steps Towards a Global Sustainable Tech Ecosystem
A process for finding an environmentally sustainable solution to e-waste demands global collaboration. Important steps include:
- Stronger E-Waste Regulation: Governments must enforce stricter rules on how to dispose of electronic waste, as well as recycling.
- Investment in infrastructure recycling: The infrastructure investment in recycling and the expansion of the availability of reliable recycling facilities that have been certified.
- Public Education and Awareness: to promote responsible behavior among consumers through awareness-raising campaigns.
With the intersection of technology advances along with regulations and the participation of customers, soon managing E-waste could be sustainable and profitable.
Conclusion: Taking Action to Combat the E-Waste Crisis
The issue of e-waste has become a growing concern, but smaller, planned steps could lead to significant changes. Individuals and organisations are crucial in reducing the amount of e-waste and encouraging the sustainable use of waste.
Practical Steps for Individuals and Organizations
Individuals:
- Extend device lifespan: Extend the Life of your device and repair it instead of purchasing an entirely new model.
- Donate or resell: Give old devices a second life.
- Dispose of E-Waste responsibly: Responsibly recycle your electronic waste through recycling programs that are certified to ensure the safety of disposal.
For businesses:
- adopt an IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) service: Securely recycle and refurbish equipment.
- Adopt sustainable tech policies: Encourage sustainable purchasing and disposal techniques.
- Instruct employees: Make them aware of ways to reduce the amount of electronic waste.
Supporting Certified E-Waste Recycling Programs
The selection of an e-waste recycler who is accredited will guarantee that your electronic waste gets disposed of responsibly. Find certifications like:
- R2 (Responsible Recycling) Standard
- e-Stewards Certification
- WEEE Compliance (for European regulations)
Through assisting the programs, you can prevent the illegal disposal of waste, protect the environment and make certain that valuable materials are properly recycled to be reused.
Final Thought
The best way to achieve the goal of having an environmentally sustainable method of disposing of E-waste starts with understanding the problem and then implementing it. Whatever your situation, whether a person or a company, making a conscious decision today will make a more healthy and environmentally sustainable technology future.
For a deeper understanding of ethical e-waste management and best practices, check out our Guide to IT Asset Disposition to learn how businesses can implement sustainable and compliant ITAD strategies.
